
So along the east coast of Australia, including the east coast of Tasmania, it is roughly a northeaster along western coasts it is a southwester (for example: the Fremantle Doctor) along northern coasts it is a northwester and on southern coasts the breeze will end up as a southeaster. The final sea breeze direction ends up blowing along the shore at an angle of about 20 to 30 degrees from the general direction of the shoreline across the southern half of Australia, and 40 to 50 degrees from the shoreline in the tropics where this backing effect is reduced (the Coriolis Effect is weaker). This “backing” will tend to be most rapid during the first hour and is largely complete after 2 to 3 hours, although it will continue to back slowly until the sea breeze dies. Here we would see the sea breeze start up mid to late morning as a light wind blowing directly onshore and its direction will shift to the left (or “back”) during the afternoon as the speed increases. This situation, assuming little or no gradient wind (the wind at around 900m above the earth’s surface), is the pure sea breeze situation where the average speed gets up to around 15kt. If there is a reasonably thick layer of flat stratocumulus cloud with the high-pressure system, the sea breeze will be further weakened.ĭuring an unstable weather situation, often with a low pressure system or trough close by, or where we have cold air sitting over a warmer sea, the sea breeze circulation will progressively grow to a height around 900 to 1000m above the surface. Thus the sea breeze will be weaker than average, around 10 to 12 kts, and will not extend as far offshore. This means that the upper return flow will be confined to a low height, around 500m, which limits the size of the sea breeze circulation. During a stable situation, such as that normally associated with the first arrival of a high-pressure system, a shallow temperature inversion can act as a lid on the sea breeze.

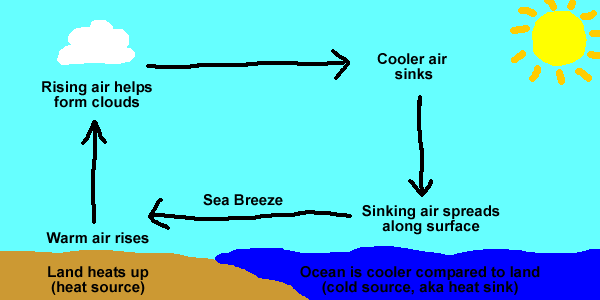
The peak speed, usually experienced around mid to late afternoon, depends mainly on the nature of the stability of the air and the magnitude of the temperature gradient between air over the sea and the air over the land, with the former determining the depth of the circulation. Typically you will find the breeze extends out 50 to 60 km offshore by mid-afternoon, with the speed increasing from a few knots at the seaward extremity to 15 to 20 kts near the coast. More air subsides near the coast, with less further out to sea, leading to a fresher sea breeze near the coast that weakens as you move off shore. In pure sea breezes, with a great seawards extent, the greatest temperature gradient is near the coast. Figure 1 shows a simplified sea breeze circulation cell.Īs time passes by, the circulation increases in extent - both offshore and onshore, and deepens. So the sea breeze circulation actually starts above the surface. Air gradually subsides or sinks over the sea as it cools, taking the place of the air that is beginning to move towards the coast - the sea breeze. Provided there is no significant wind at this level, the air will have a natural tendency to flow seawards to reduce this imbalance. This causes an accumulation of air (an imbalance of pressure) at some higher level, usually between 3 metres. Sure - during most mornings, the sun heats up the land surface warm air does expand and hence rises.
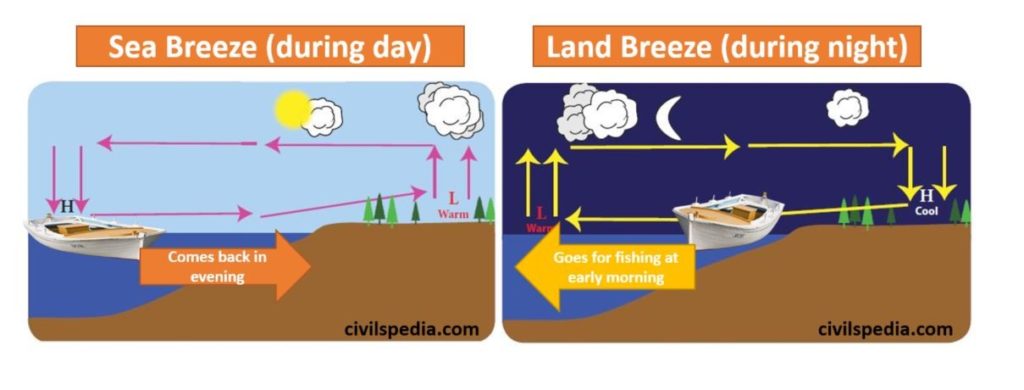
This is OK as far as it goes, but is not a complete enough explanation. This movement of cooler air was dubbed the sea breeze. When we were at school, quite a number of years ago now, we were taught that the sea breeze simply came about because the land heated up during the morning, hot air rose as a consequence and was replaced by cooler air coming in off the water. However, the theory is sound, if reversed, in the Northern Hemisphere. But we will have a good try at explaining the more interesting features! The information in this article pertains to the Southern Hemisphere and refers to Australia.
The answers aren’t that simple because the sea breeze circulation has numerous variations. How many times have you been sitting out on the water pondering the key questions about life - such as why the sea breeze refused to show up or, more importantly, had arrived but had rapidly built to a much stronger breeze than you anticipated? How often have you been jogging along a beach somewhere, sweating profusely, but consoled by the knowledge that the local afternoon sea breeze will be making its daily visit very soon to cool you down - without fully understanding just how and why the breeze will arrive?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
